Create your first automation in just a few minutes.Try Studio Web →
Enquero - File Path Access Validator
by YouTube
1
Snippet
<100
Summary
Summary
Handle the file path pre-validation need and the access permission from the beginning of a BOT development cycle
Overview
Overview
BOT users are often required to access different physical and network shared file paths for various file I/O operations, especially when working with MS Excel, CSV or PDF files. For these shared directories and sub-directories access permissions can be defined by the IT administrators through Group Policies.
Usually, business requirements stipulate that the BOT process is required to access file paths, to read or write files from/to the source/destination address respectively.
Still, many of these BOT processes fail during development or when migrated to the test/production servers as the file paths access permissions are not set up as expected.
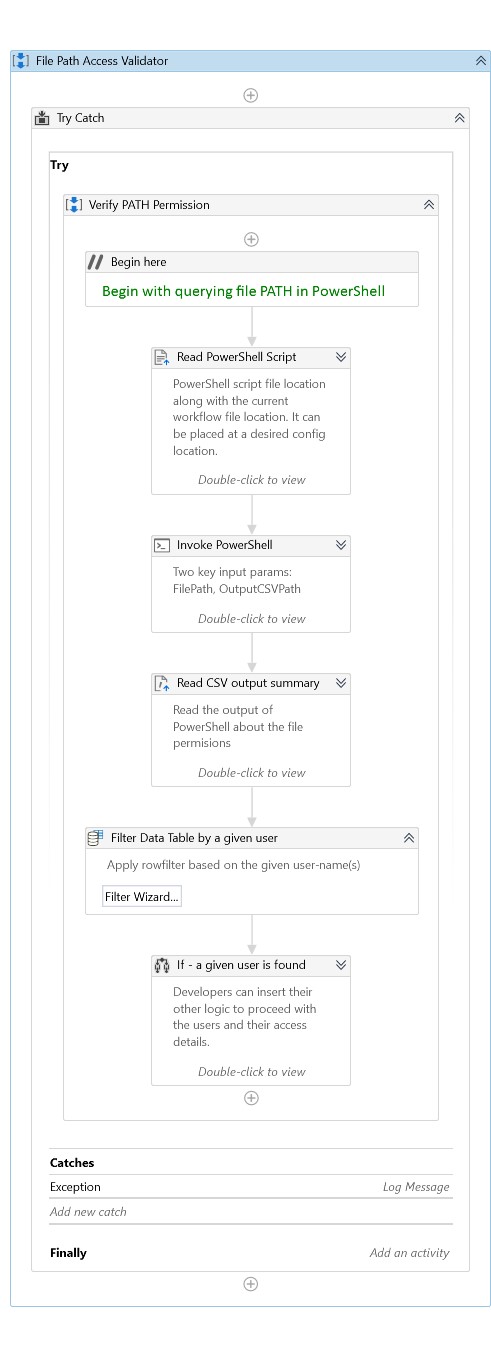
The FilePathAccessValidator workflow is developed using a Windows PowerShell script. The inbuilt Invoke PowerShell activity from UiPath executes the PowerShell script to query Windows Folder object and list user permission details.
As input you need to add the below file paths:
- read access permission details
- save the CSV file summary output.
Developers can read the permission details from the CSV file and tailor the workflow.In the attached workflow, its usage is also illustrated with a hypothetical use case to query and print the user’s permission details in logs.
Features
Features
The advantages of using the File Path Access Validator include: Query the user access details of the file path (directory, sub-directories, network shared path, etc.) Verify if a given user (say, a BOT user) has any read-write access to the file path or not Most useful when a BOT user's access to the file path(a network shared directory, sub-directories for file I/O operations) needs to be queried and verified after the Init state in ReFramework Reusable across different projects and workflows
Additional Information
Additional Information
Dependencies
Windows PowerShell ExecutionPolicy Windows PowerShell has an inbuilt security setting called "execution policy". Execution Policy determines how (or if) a given PowerShell script can run. By default, PowerShell's execution policy is set to "Restricted", which means the script will not run. You can verify the currently set execution policy by querying on a PowerShell command console as: Get-ExecutionPolicy. It will tell the execution right of the currently logged in user. You need to change the behavior of a PS script execution from the PowerShell command console as: Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned. You should be able to execute PowerShell scripts then. Else, you can check with your IT team.
Code Language
Visual Basic
License & Privacy
MIT
Privacy Terms
Technical
Version
1.0.0Updated
February 18, 2020
Works with
Tested with: UiPath Studio 2019.12.0-beta.61 Windows 10 OS Windows PowerShell Version 5.1.18362.145
Certification
Silver Certified
Support
UiPath Community Support
Resources